Oleksii Trekhleb | Javascript algorithms (Counting sort)
This is a series of books diving deep into the core mechanisms of the JavaScript language.
· 2 phút đọc.

In computer science, counting sort is an algorithm for sorting a collection of objects according to keys that are small integers; that is, it is an integer sorting algorithm. It operates by counting the number of objects that have each distinct key value, and using arithmetic on those counts to determine the positions of each key value in the output sequence. Its running time is linear in the number of items and the difference between the maximum and minimum key values, so it is only suitable for direct use in situations where the variation in keys is not significantly greater than the number of items. However, it is often used as a subroutine in another sorting algorithm, radix sort, that can handle larger keys more efficiently.
Because counting sort uses key values as indexes into an array, it is not a comparison sort, and the Ω(n log n) lower bound for comparison sorting does not apply to it. Bucket sort may be used for many of the same tasks as counting sort, with a similar time analysis; however, compared to counting sort, bucket sort requires linked lists, dynamic arrays or a large amount of preallocated memory to hold the sets of items within each bucket, whereas counting sort instead stores a single number (the count of items) per bucket.
Counting sorting works best when the range of numbers for each array element is very small.
Algorithm
Step I
In first step we calculate the count of all the elements of the input array A. Then Store the result in the count array C. The way we count is depicted below.
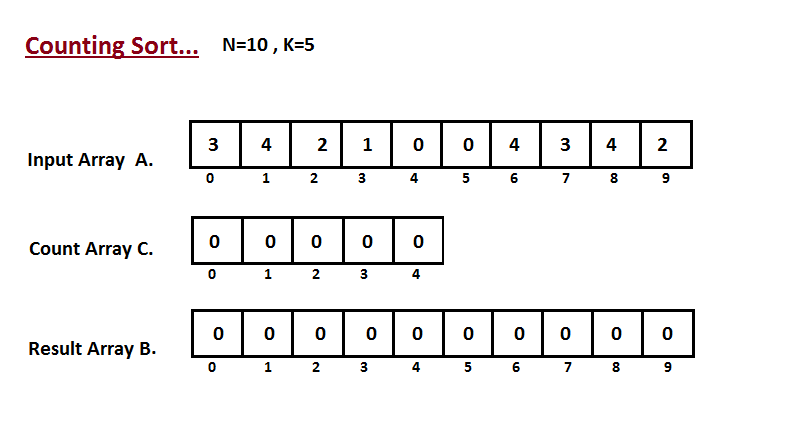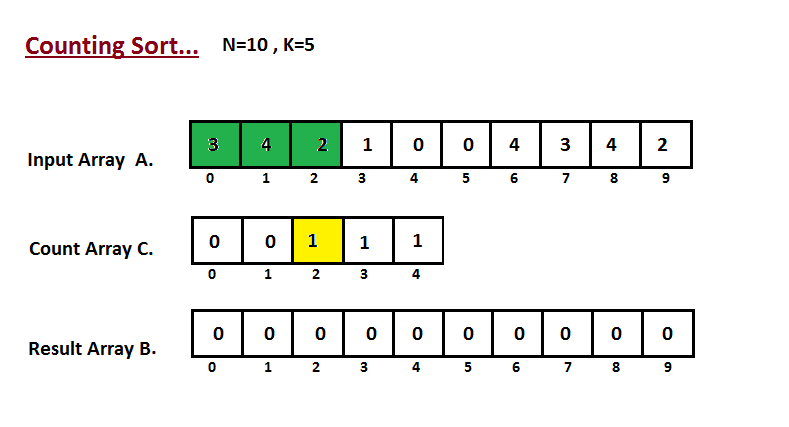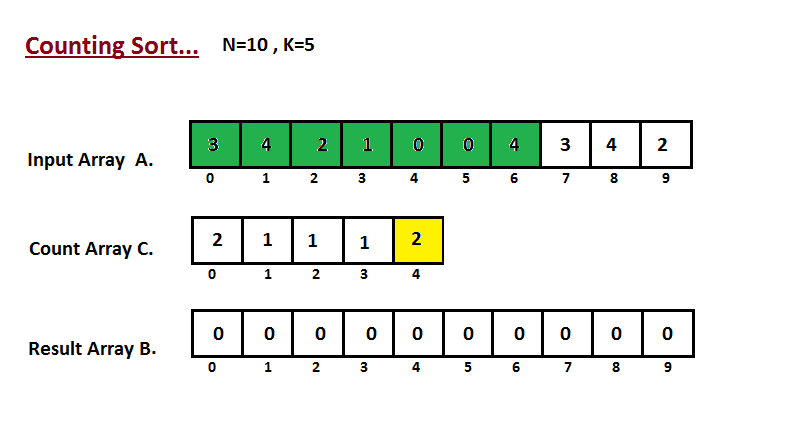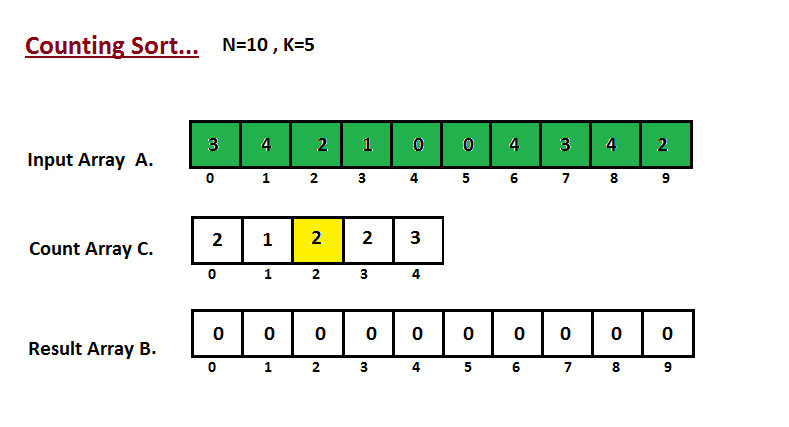
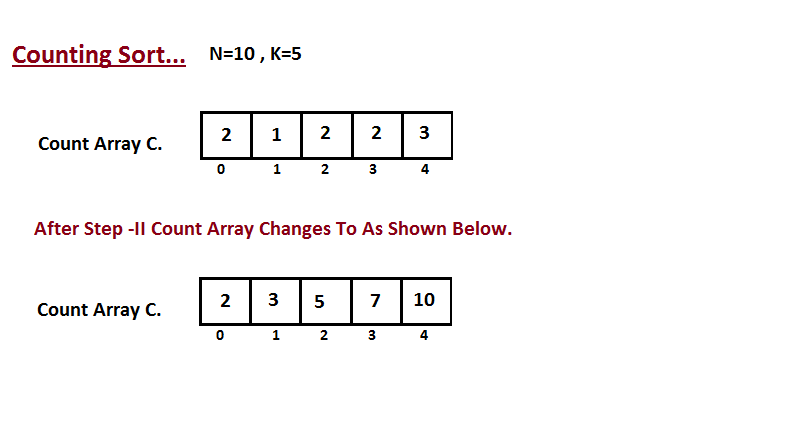
Step II
In second step we calculate how many elements exist in the input array A which are less than or equals for the given index. Ci = numbers of elements less than or equals to i in input array.
Step III
In this step we place the input array A element at sorted position by taking help of constructed count array C ,i.e what we constructed in step two. We used the result array B to store the sorted elements. Here we handled the index of B start from zero. 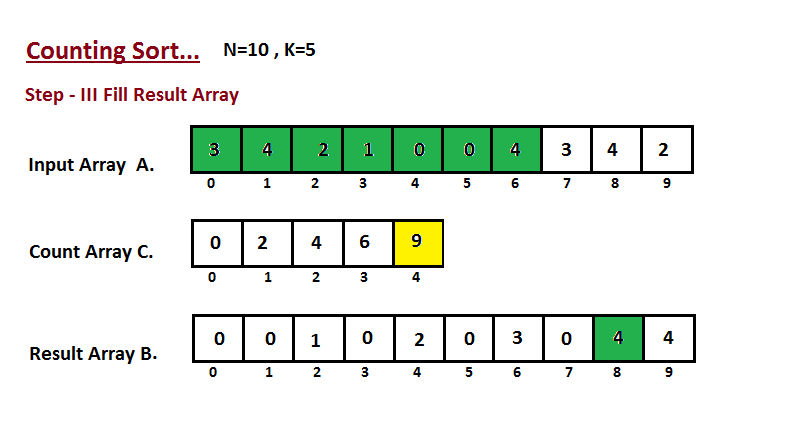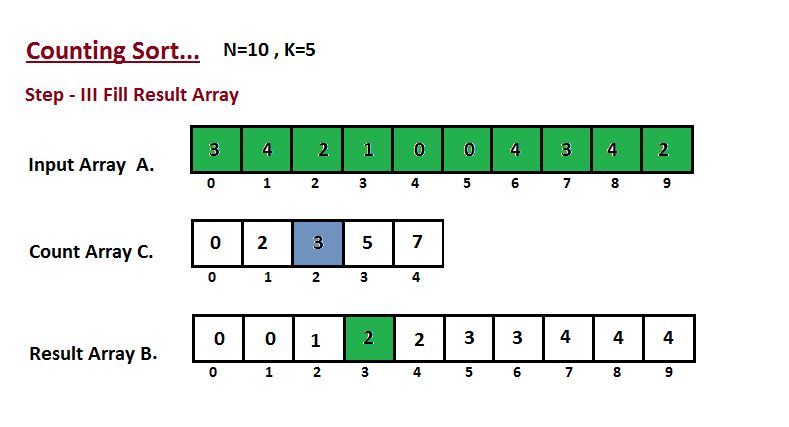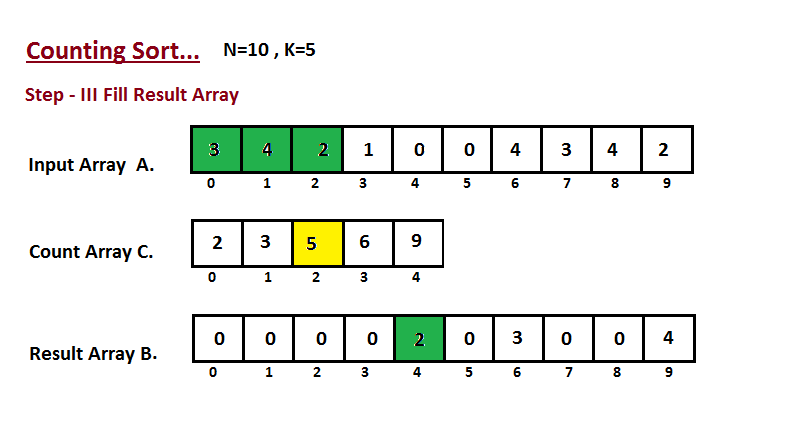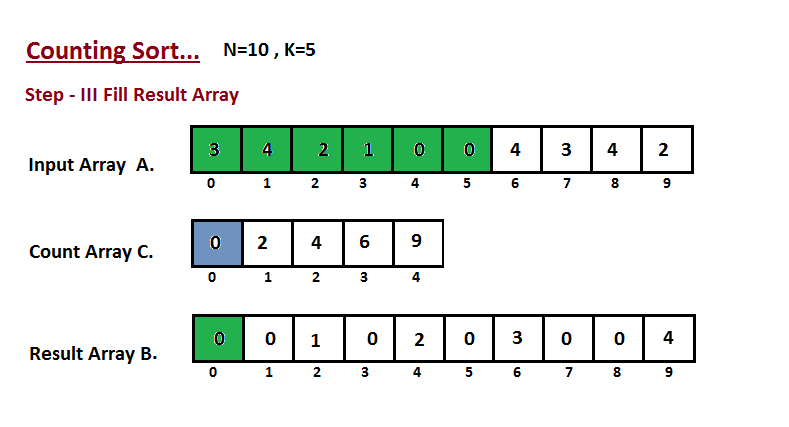
Complexity
| Name | Best | Average | Worst | Memory | Stable | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Counting sort | n + r | n + r | n + r | n + r | Yes | r - biggest number in array |






