Oleksii Trekhleb | Javascript algorithms (Rain terraces problem)
This is a series of books diving deep into the core mechanisms of the JavaScript language.
· 3 phút đọc.

Given an array of non-negative integers representing terraces in an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
Examples
Example #1
Input: arr[] = [2, 0, 2]
Output: 2
Structure is like below:
| |
|_|
We can trap 2 units of water in the middle gap.
Example #2
Input: arr[] = [3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 4]
Output: 10
Structure is like below:
|
| |
| | |
|__|_| We can trap _32 units_ of water between 3 an 2,
_1 unit_ on top of bar 2 and _3 units_ between 2 and 4. See below diagram also.
Example #3
Input: arr[] = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
Output: 6
Structure is like below:
| | || |
_|_||_||||||
Trap _1 unit_ between first 1 and 2, _4 units_ between
first 2 and 3 and _1 unit_ between second last 1 and last 2.
The Algorithm
An element of array can store water if there are higher bars on left and right. We can find amount of water to be stored in every element by finding the heights of bars on left and right sides. The idea is to compute amount of water that can be stored in every element of array. For example, consider the array [3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 4], We can trap 32 units of water between 3 an 2, 1 unit on top of bar 2 and 3 units between 2 and 4. See below diagram also.
Approach 1: Brute force
Intuition
For each element in the array, we find the maximum level of water it can trap after the rain, which is equal to the minimum of maximum height of bars on both the sides minus its own height.
Steps
- Initialize
answer = 0 - Iterate the array from left to right:
- Initialize
max_left = 0andmax_right = 0 - Iterate from the current element to the beginning of array updating:
max_left = max(max_left, height[j]) - Iterate from the current element to the end of array updating:
max_right = max(max_right, height[j]) - Add
min(max_left, max_right) − height[i]toanswer
- Initialize
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity: O(n^2). For each element of array, we iterate the left and right parts.
Auxiliary space complexity: O(1) extra space.
Approach 2: Dynamic Programming
Intuition
In brute force, we iterate over the left and right parts again and again just to find the highest bar size up to that index. But, this could be stored. Voila, dynamic programming.
So we may pre-compute highest bar on left and right of every bar in O(n) time. Then use these pre-computed values to find the amount of water in every array element.
The concept is illustrated as shown:
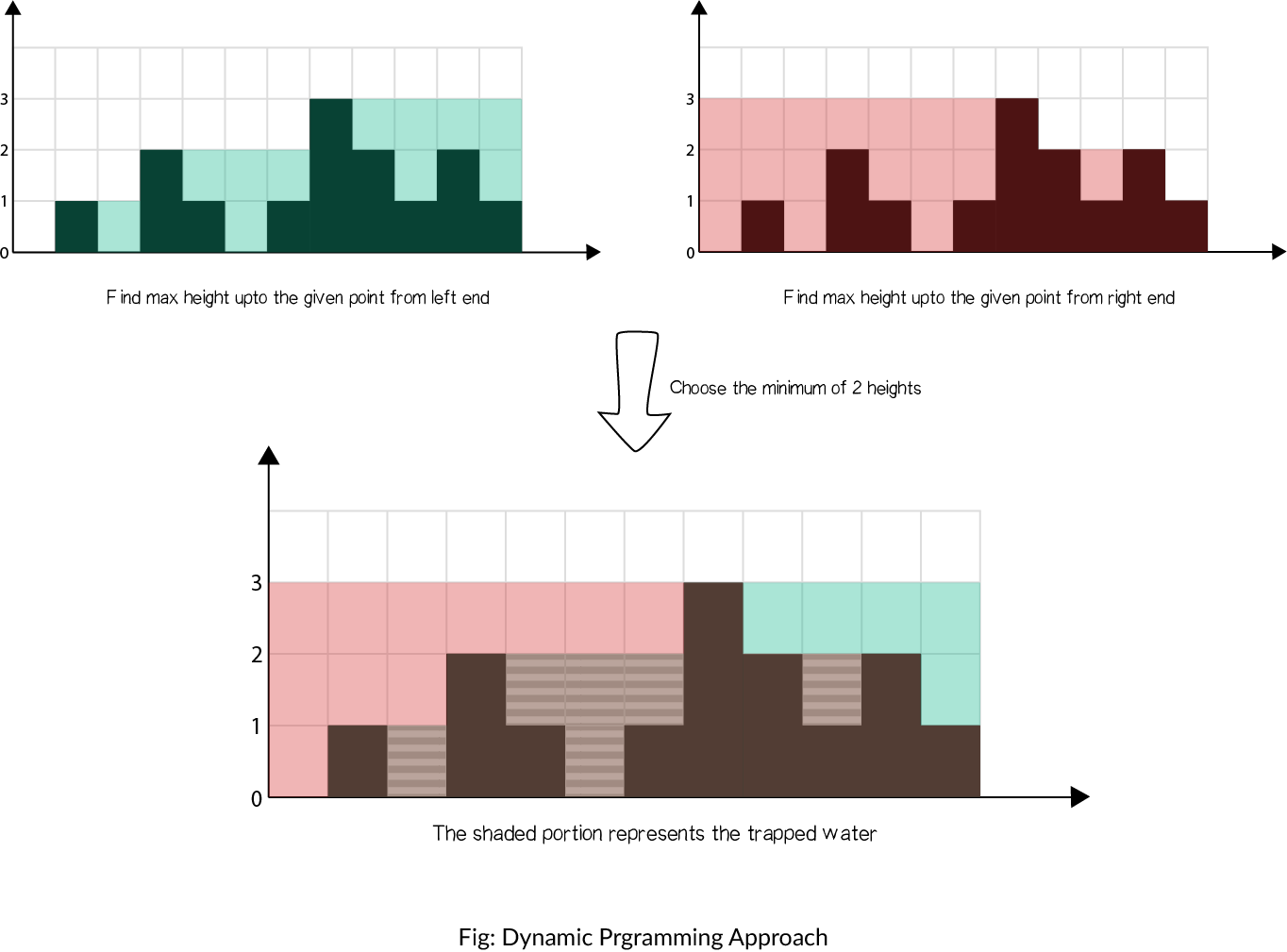
Steps
- Find maximum height of bar from the left end up to an index
iin the arrayleft_max. - Find maximum height of bar from the right end up to an index
iin the arrayright_max. - Iterate over the
heightarray and updateanswer:- Add
min(max_left[i], max_right[i]) − height[i]toanswer.
- Add
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity: O(n). We store the maximum heights upto a point using 2 iterations of O(n) each. We finally update answer using the stored values in O(n).
Auxiliary space complexity: O(n) extra space. Additional space for left_max and right_max arrays than in Approach 1.






